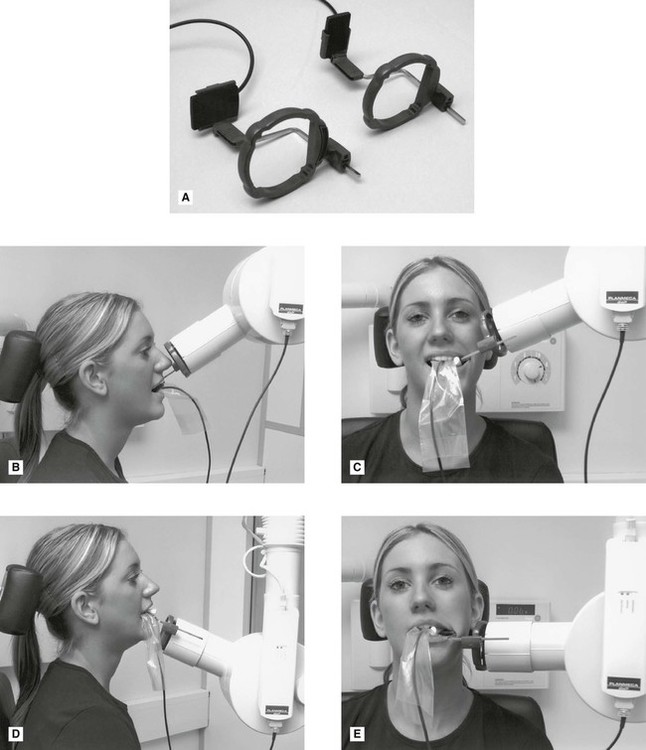
Bitewing X-rays show details of the upper and lower teeth in one area of the mouth. The image receptor is placed in a holder and positioned in the mouth parallel to the long axis of the tooth under.
Periapical Radiography Clinical Gate
Periapical radiography is a commonly used intraoral imaging technique in radiology and may be a component of your radiologic examination.
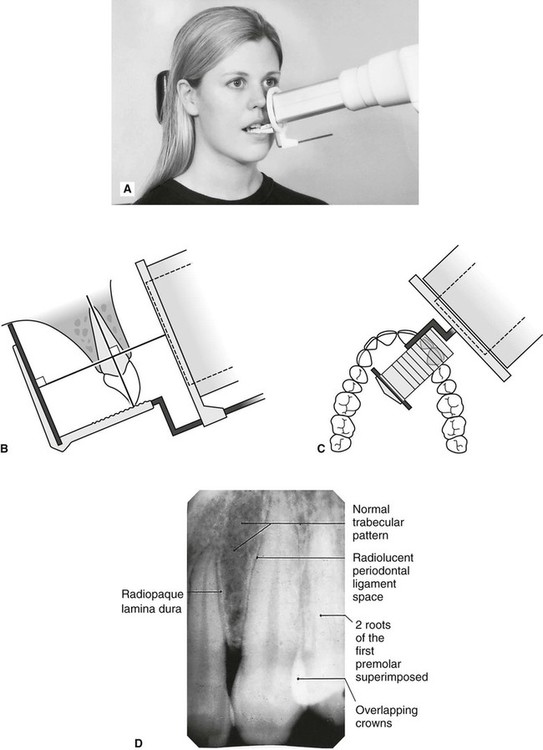
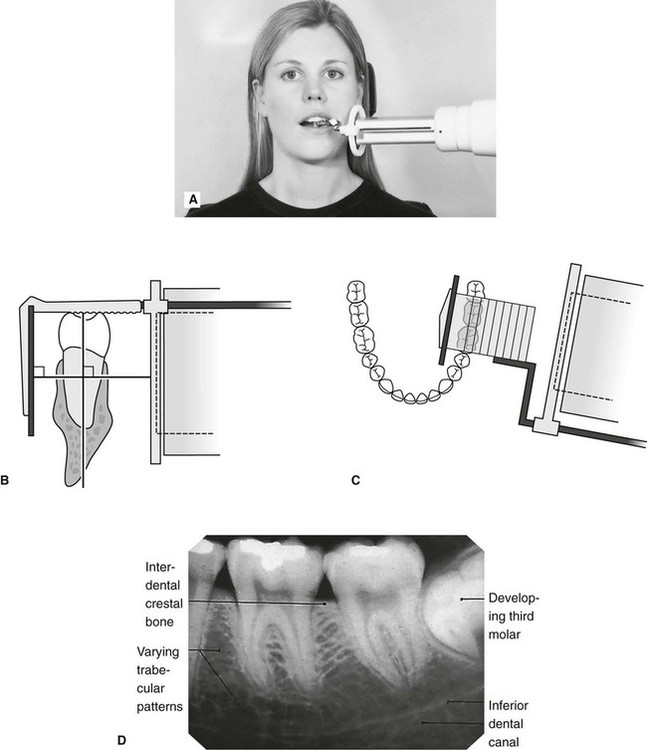
. It shows everything from the crown chewing surface to the root below the gum line. The patient is seated upright in the dental chair and should remove any removable dental appliances glasses or jewelry that could interfere with the X-ray beam. Periapical film is held parallel to the long axis of the tooth using film-holding instruments.
Each bitewing shows a tooth from its crown the exposed surface to the level of the supporting bone. The central ray is directed to pass at a perpendicular angle to both the tooth and the film. First to diagnosis periapical lesions a thorough clinical examination about dental caries tooth mobility vertical percussion sinus tract and X-ray is required.
Periapical radiographs provide important information about the teeth and surrounding bone. The patient was positioned upright with hisher mouth was opened as wide as possible to allow the X-ray beam to pass to the sensor unobstructed from the opposite side of the mouth. Each periapical x-ray shows a small section of your upper or lower teeth.
Bitewing Film The patient bites on to hold the film in place. Radiographic techniques 1. The extraoral periapical radiographic technique was performed for both maxillary and mandibular teeth using Newman and Friedman technique2.
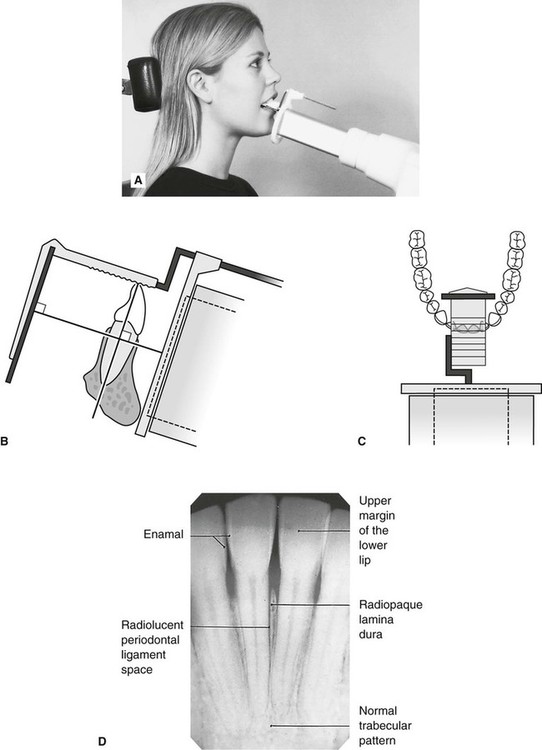
The Bisecting Angle Technique is an alternative to the paralleling technique for taking periapical films. RADIOGRAPHS Periapical Bitewing Occlusal 2. The X-ray is taken and the exposed plate is then loaded into a scanner or processor which reads the image.
A periapical x-ray is one that captures the whole tooth. Periapical and bitewing radiographic imaging may be necessary to assess pulpal pathosis in primary molars 1232020 1 X-ray Technique Bitewing Technique. The film is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth to be radiographed and the central beam of X-ray is directed at right angle to the film and the teeth.
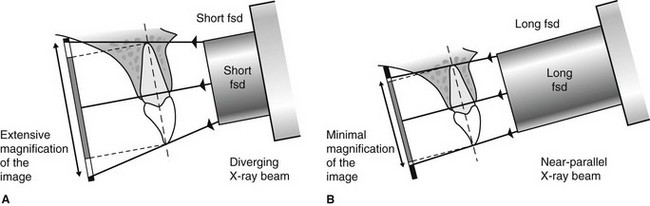
Changes to the angulation of the X-ray beam in relation to the teeth and film can help diagnosis and treatment by producing images which provide additional information not alway. With this technique the film is placed parallel to the long axis of a tooth allowing the X-ray to be focused perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth. Periapical film is held parallel to the long axis of the tooth using film-holding instruments.
Since the slope and curvature of the dental arches and the alveolar processes will. Ensure they are seated high enough so it is easy to see the occlusal. The X-ray head is directed at right angles vertically and horizontally of both the tooth and the image receptor.
With the proposed software only a periapical X-ray is provided so the software cannot provide a diagnosis that. Most frequently used radiography is for the periapical which is performed by the bisecting Thus when considering the execution of the radiographic technique and the possibility of errors that occur during the exposure of X-ray image XR receptors it is important to identify those that occur more frequently. Students are given a demonstration of panoramic radiology.
The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays. The bisecting short-cone and paralleling long-cone techniques are two of the most commonly used techniques. Assessment of root formation n completion.
Film development and mounting are discussed and practiced. The film is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth in question and the central x-ray beam should be directed perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth. Assessment of relationship of roots to various vital structures.
These x-rays are often used to detect any unusual changes in the root and surrounding bone structures. Single periapical radiographs are often made of individual teeth or groups of teeth to obtain information for treatment or diagnosis of localized diseases or abnormalities. Students learn how to expose dental periapical x-ray film using the Rinn Paralleling Technique using the XCP film holder.
The film is placed parallel to the long axis. The accelerated x-rays are decelerated by the target material resulting in bremsstrahlung. Fitzgerald called as paralleling or long cone technique.
Assessment of root morphology. Implant site assessment and. A long cone is used to take x-rays with paralleling exposure techniques.
Periapical views are used to record the crowns roots and surrounding bone. Periapical views are used to record the crowns roots and surrounding bone. For this purpose a special technique of periapical radiography was developed by Gordon M.
The paralleling technique is recommended for routine periapical radiography but there are. Each periapical X-ray shows all teeth in one portion of either the upper or lower jaw. By using a film sensor holder with still.
DENTAL X-RAYS X-rays are produced by boiling off electrons from a filament the cathodeand accelerating the el to the target at the anode. Different techniques and instruments are used to drain and decompress large periapical lesions ranging from placing a stainless steel tube into the root canal exhibiting persistent apical exudation 202 204 which is non-surgical decompression to placing polyvinyl or polyethylene tubes through the alveolar mucosa covering the apical lesion which is surgical. To take a periapical exposure the hygienist or x-ray technician places a small photosensitive imaging plate coated with phosphorus into a sterile wrapper and inserts it into the patients mouth just like a conventional X-ray film card.
The X-ray tubehead is then aimed at right angles vertically and horizontally to both the tooth and the image. Parallel technique The image receptor is placed in a holder and placed in the mouth parallel to the longitudinal axis of the tooth under. The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays.
Both techniques have advantages and disadvantages. The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays. The sensor was placed on the.
Periapical radiographic techniques during endodontic diagnosis and treatment Int Endod J. By using a filmsensor holder with fixed image receptor and.
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
7 Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry

Periapical Radiography Clinical Gate
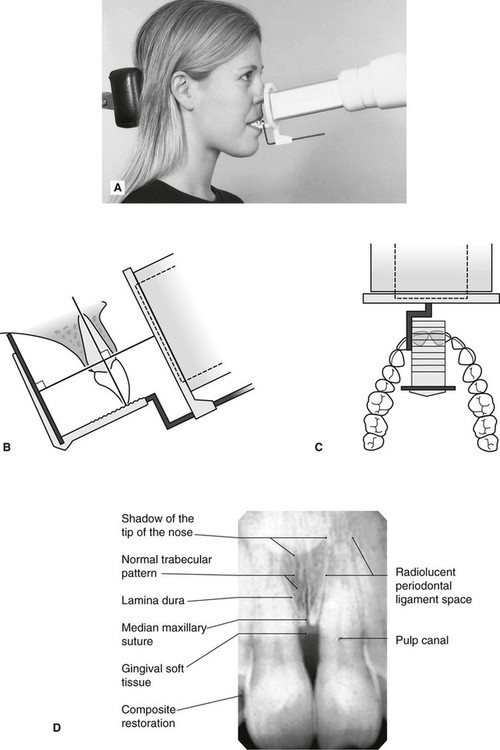
Periapical Radiography Clinical Gate
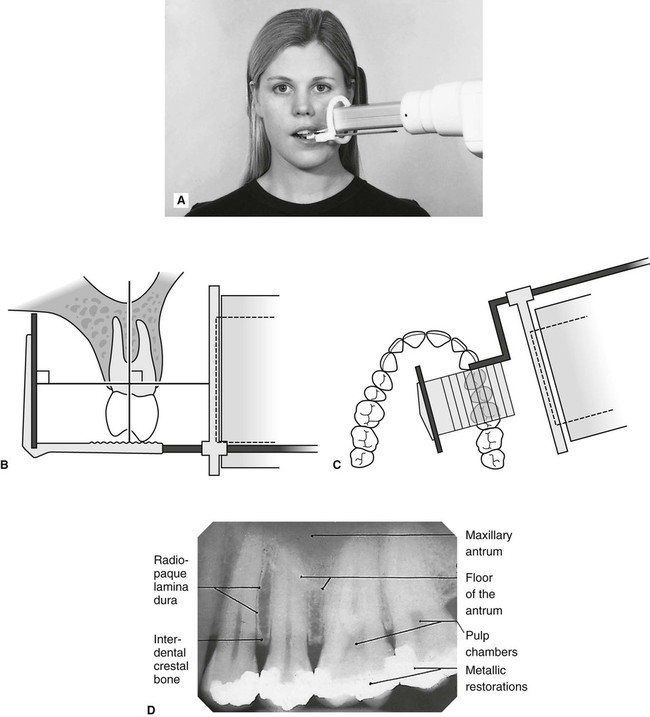
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
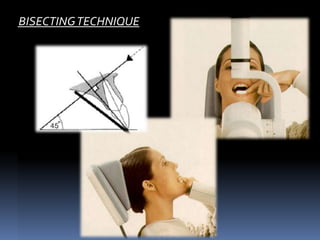
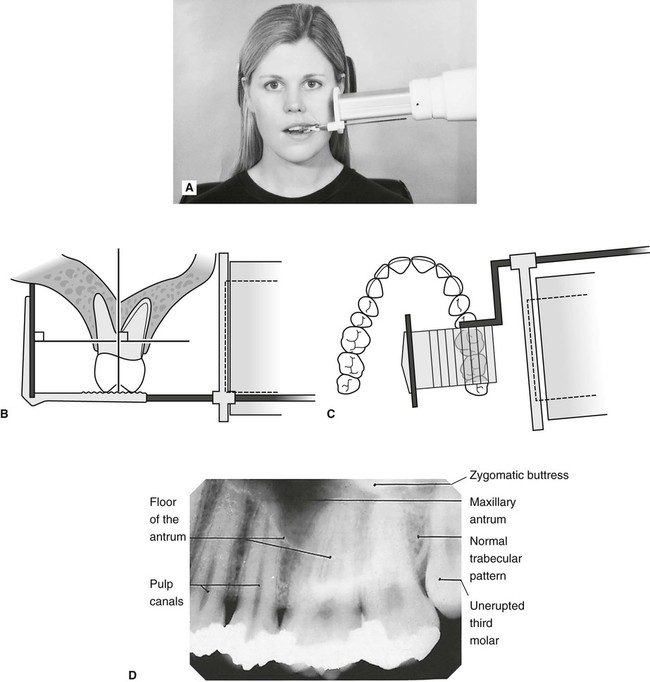
0 comments
Post a Comment